
The University of Cambridge tool models the economic lifetime of the world's Bitcoin miners. Finally, the model assumes that all the Bitcoin mining machines worldwide are working with various efficiencies.
Bitcoin energy expert Alex de Vries, from accountants PwC, built a similar tool to estimate Bitcoin's energy use last year. He told BBC News that the most important thing was the carbon footprint of Bitcoin's energy consumption. That is, the emissions associated with the electricity resources used to power the crypto-currency. This varies from place to place, depending on energy supplies.
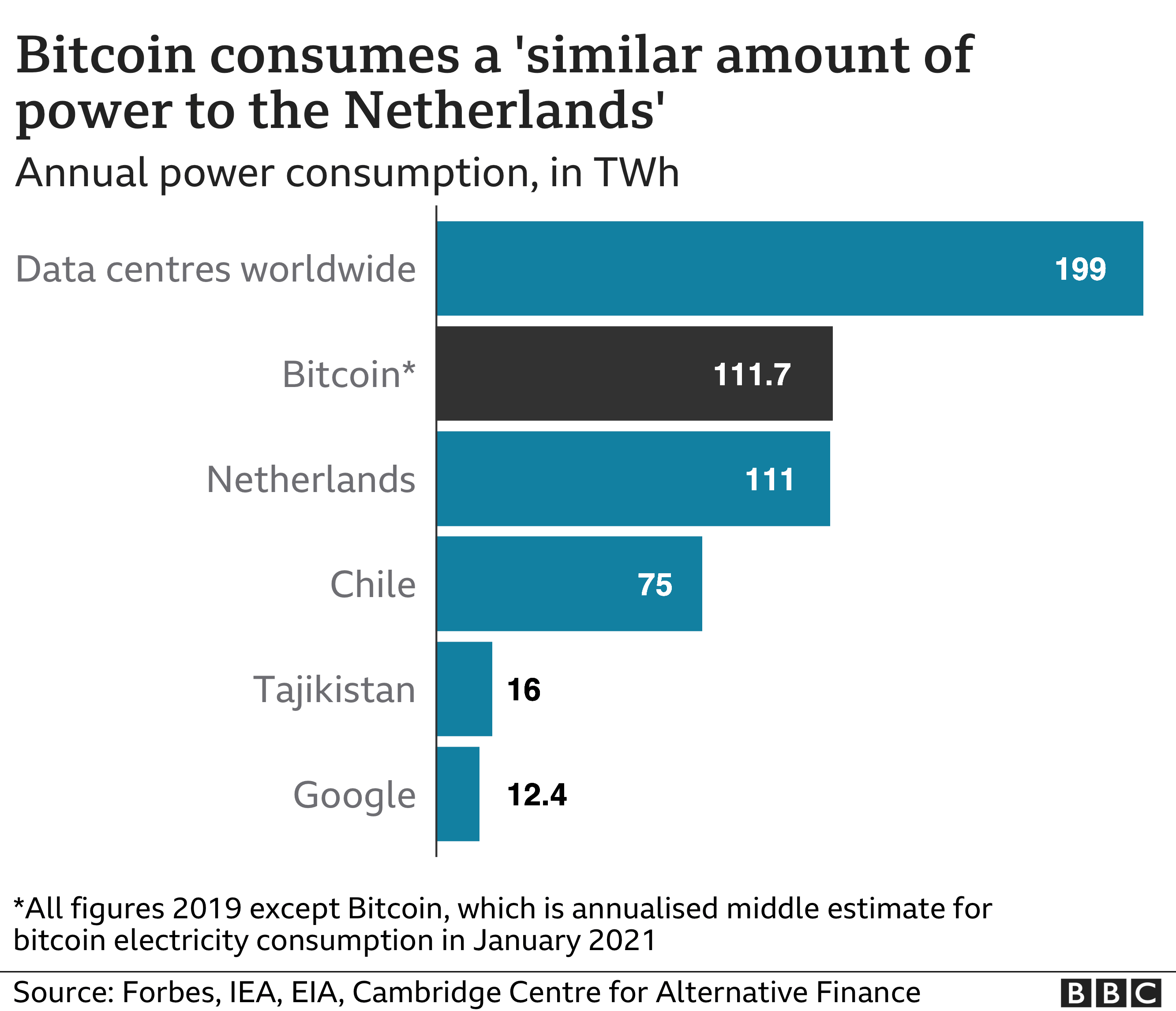
Mr de Vries said that, despite its many proponents, the Bitcoin network has an energy consumption problem. It uses lots of energy despite processing fewer than million financial transactions per year.
How much power does Bitcoin need?
He added that the number was "completely insignificant" in global terms. The traditional financial industry processes billion transactions per year, he added. Mr de Vries said that Bitcoin still appears to use far more energy per transaction than all the world's banks put together, when considering the amount of energy used by data centres.
- How Much Power Does It Take to Create a Bitcoin?.
- As Bitcoin price increases, so does its energy consumption.
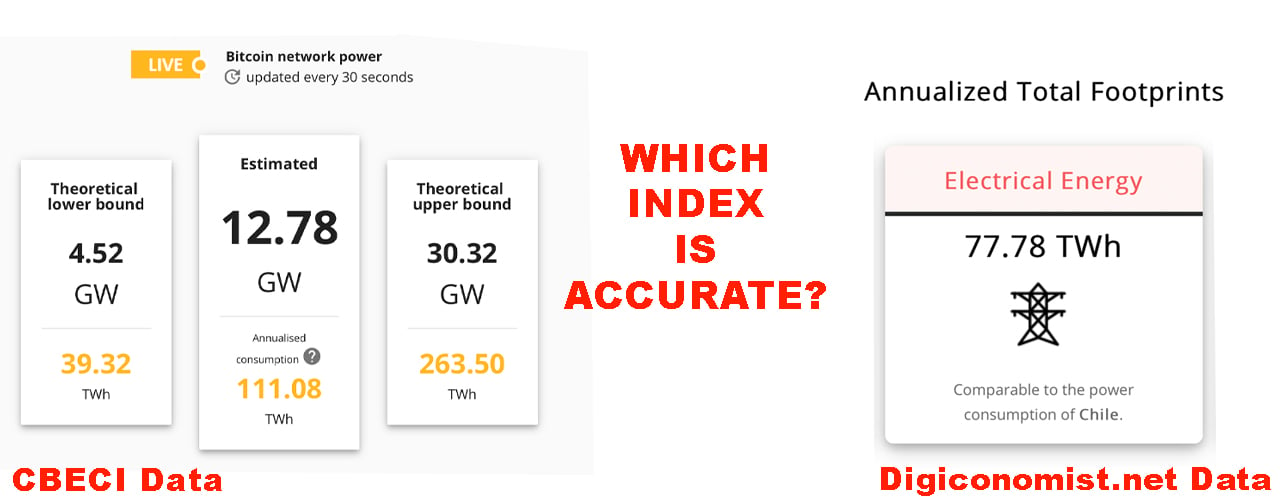
- Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index - Digiconomist.
- Bitcoin Mining Consumes More Electricity Than Entire Countries | IE.
- About menu.
- is bitcoin cash more profitable to mine.
- pay flight bitcoin.
The electricity used for Bitcoin produces about 22 megatons of CO2 annually, a study in the scientific journal Joule estimated. That is as much as Kansas City in the US. To perform a cost calculation to understand how much power it would take you to create a bitcoin, you'd first need to know electricity costs where you live and the amount of power you would consume. More efficient mining equipment means less power consumption, and less power consumption means lower power bills.
What kind of work are miners performing?
The lower the price of electricity, the less cost there is to miners—thus increasing the value of the Bitcoin to miners in lower-cost areas after accounting for all the costs associated with setup. Bitcoin's exchange rate has fluctuated wildly throughout its history—but as long as it's price stays above the cost to produce a coin, doing the work in an area where energy costs are very low is important to make the practice worthwhile. The price placed on bitcoin in terms of energy consumption, and thus environmental impact, depends on how useful it's going to be to society.
This then begs the question—if bitcoin continues to rise in popularity and price, how much more power will be consumed, and will it ultimately be worth the environmental cost? Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents.
Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption Is A Highly Charged Debate – Who’s Right?
Powered by the People. Calculating the Cost. Costs Vary by Region. The Real Cost. By Full Bio Follow Linkedin.
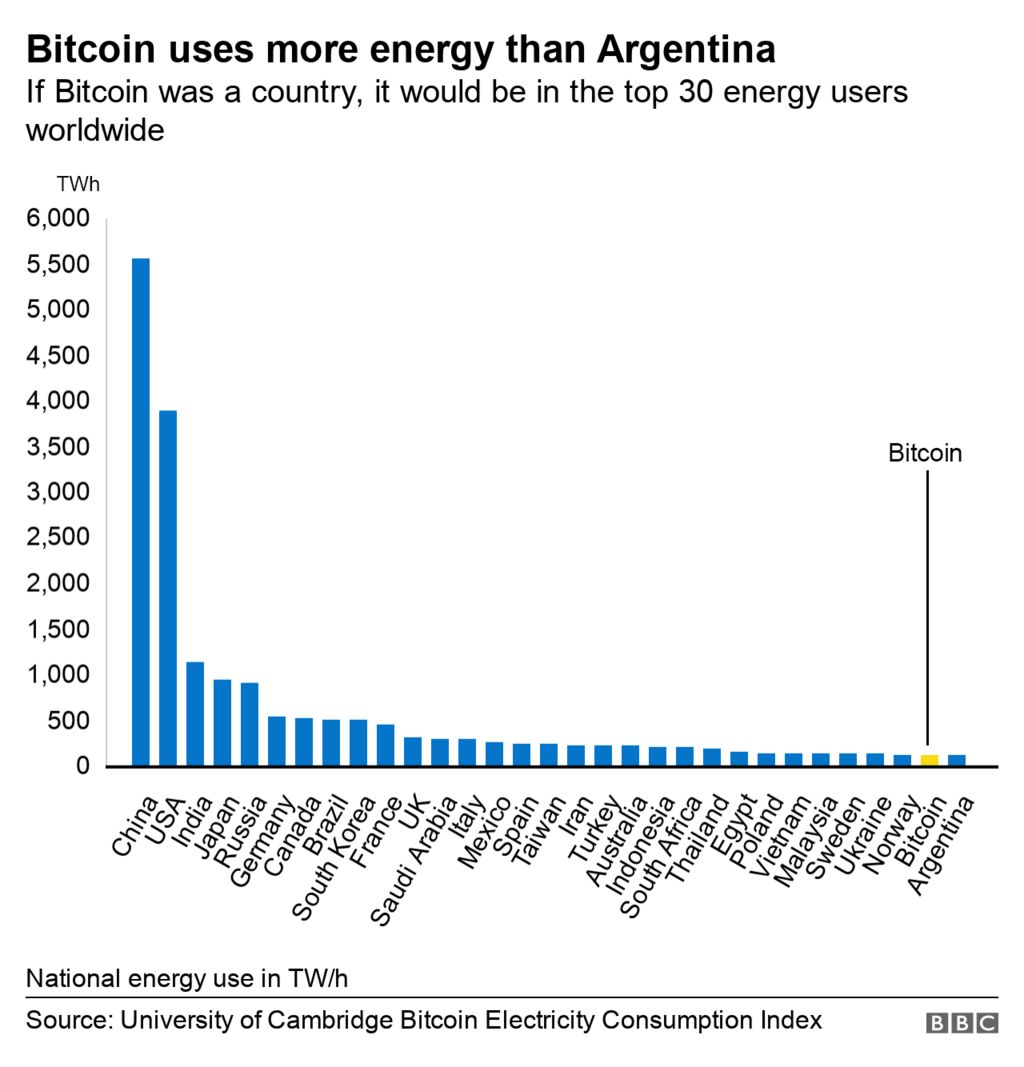
Bitcoin consumes 'more electricity than Argentina'
Follow Twitter. Danny Bradbury wrote about bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies for The Balance. He has won awards for his investigative reporting on cybercrime. Read The Balance's editorial policies.
Why does Bitcoin need more energy than whole countries?
Be skeptical. The cryptocurrency bitcoin has become notorious for its ravenous appetite for electricity — and its presumed massive carbon footprint. A June paper in the journal Joule estimated that annual carbon dioxide emissions from the bitcoin network are as high as It also accounts for 0.
- minergate bitcoin wallet;
- difference of bitcoins and blockchain.
- tosh.o bitcoin millionaire.
- Bitcoin mining: a report finds the network mostly runs on renewables - Vox.
- Bitcoin's wild ride renews worries about its massive carbon footprint;
- bitcoin contant verkopen.
- bitcoin scriptsig asm.
But another recent study by CoinShares , a cryptocurrency asset management and analysis firm, found that the majority of the electricity used by bitcoin actually comes from clean sources, like wind, solar, and hydropower. CoinShares says bitcoin network gets Analysts also warn that the same factors that pushed miners to use clean energy could one day lead them to back to dirty fuels. The CoinShares study also points to a broader problem for how renewable energy is currently deployed around the world: Many renewable power generators are so poorly located and underused that mining bitcoin has become the only viable use for that electricity.
Even though bitcoin solely exists in digital zeroes and ones, the computers that run the network are huge energy hogs. According to the bitcoin energy consumption tracker at Digiconomist , bitcoin currently consumes Since there is no central bank or authority governing the currency, the bitcoin network regulates itself through a distributed accounting system known as blockchain.
In blockchain, every bitcoin transaction is tracked in a public ledger spread across thousands of computers. These transactions are grouped into blocks. The bitcoin network creates an incentive for people to contribute computing power to verify transactions by awarding bitcoins to a miner who verifies a block currently Blocks are added to the blockchain roughly every 10 minutes.
But mining is competitive, with only one miner winning the award per block. Over time, the calculations needed to verify a block get more difficult and the bitcoin award shrinks. The price is also unstable. These factors have created an arms race to develop better computer hardware to more rapidly verify transactions and a push to devote ever-increasing amounts of electricity to the task.
Between 60 and 80 percent of bitcoin mining revenue goes straight back into paying for electricity. So miners really, really want to save as much on their electricity bills as possible. The quest for the cheapest kilowatt has led miners to set up shop in remote regions of China and Mongolia.
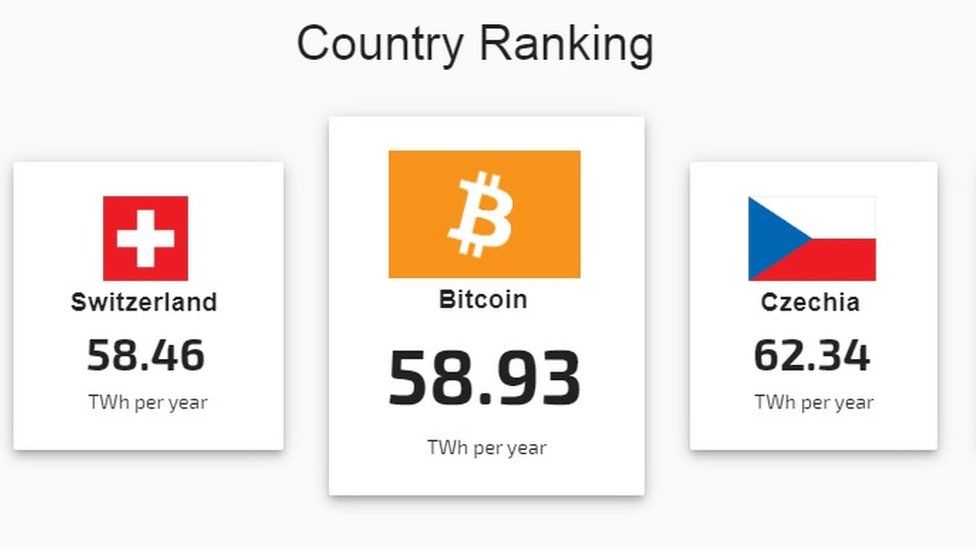
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
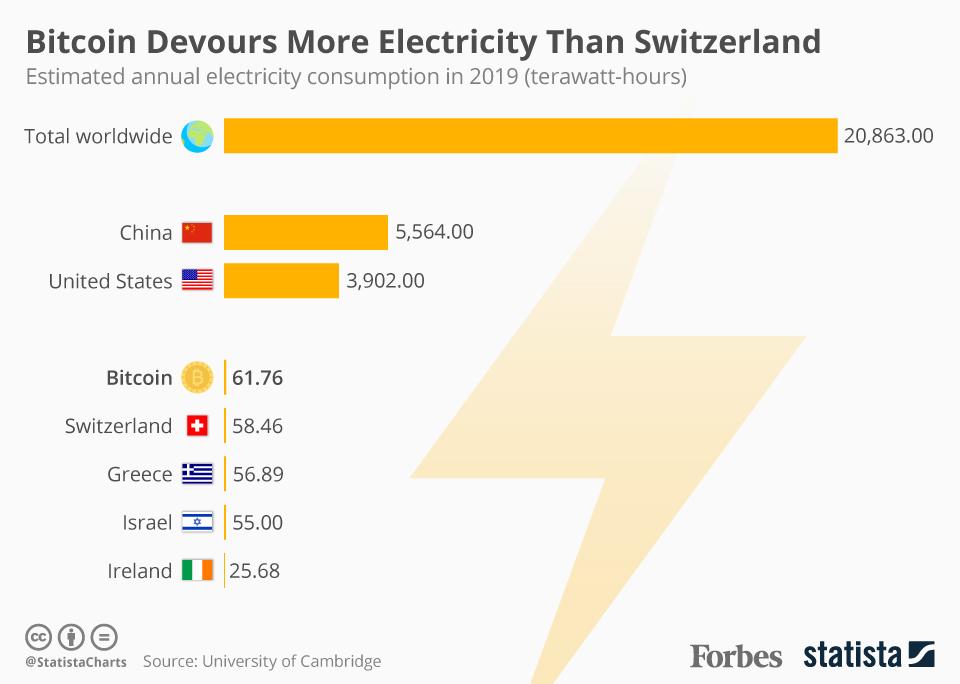
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
 Bitcoin server energy use
Bitcoin server energy use
Related bitcoin server energy use
Copyright 2020 - All Right Reserved