The private key is now imported in your wallet. You can now lock it again and close the daemon: bitcoind walletlock and bitcoind stop. Then, this answer tells you how to easily add new addresses for receiving bitcoins. Sign up to join this community. The best answers are voted up and rise to the top.
Stack Overflow for Teams — Collaborate and share knowledge with a private group. Create a free Team What is Teams? Learn more. What happens if Bitcoins are sent to a wrong, randomly generated address? Ask Question.

Asked 7 years, 9 months ago. Active 6 years, 9 months ago. Viewed 5k times. I am new to Bitcoin and I confused creating a New Address for receiving and sending payments. Here's what I did: Generated a random Bitcoin Address using www. Please help. Improve this question.
Mathias 1, 1 1 gold badge 12 12 silver badges 26 26 bronze badges. Natalie Natalie 11 1 1 silver badge 2 2 bronze badges. I don't understand, why should this be lost forever? You created the address and then forgot the password? Jun 5 '13 at If you kept the private key, you can import your coins into your wallet.
Otherwise, you've lost the coins for good. One more, quick point for clarification. Your wallet creates payment addresses for you. You do not need to create them from an external source and import them. However, since you did create a payment address bitaddress. Yes, that's a digital yell. With all of that information, someone else could steal your coins. Did you save the private key? If you didn't save the private key those coins are gone. That is why we use wallet apps like bitcoin-qt, electrum etc.
Blackmail Emails | Get Safe Online
They abstract away these technical gotchas. Add a comment. Example shows the output from running this code. Example is another example, using the Python ECDSA library for the elliptic curve math and without using any specialized bitcoin libraries. Example shows the output produced by running this script. Wallets are containers for private keys, usually implemented as structured files or simple databases. Another method for making keys is deterministic key generation.
Here you derive each new private key, using a one-way hash function from a previous private key, linking them in a sequence. As long as you can re-create that sequence, you only need the first key known as a seed or master key to generate them all. In this section we will examine the different methods of key generation and the wallet structures that are built around them.
Bitcoin wallets contain keys, not coins. Each user has a wallet containing keys. Users sign transactions with the keys, thereby proving they own the transaction outputs their coins. The coins are stored on the blockchain in the form of transaction-ouputs often noted as vout or txout.
Dusting attacks
In the first bitcoin clients, wallets were simply collections of randomly generated private keys. This type of wallet is called a Type-0 nondeterministic wallet. For example, the Bitcoin Core client pregenerates random private keys when first started and generates more keys as needed, using each key only once. The disadvantage of random keys is that if you generate many of them you must keep copies of all of them, meaning that the wallet must be backed up frequently. Each key must be backed up, or the funds it controls are irrevocably lost if the wallet becomes inaccessible.
This conflicts directly with the principle of avoiding address re-use, by using each bitcoin address for only one transaction. Address re-use reduces privacy by associating multiple transactions and addresses with each other. A Type-0 nondeterministic wallet is a poor choice of wallet, especially if you want to avoid address re-use because that means managing many keys, which creates the need for frequent backups. Although the Bitcoin Core client includes a Type-0 wallet, using this wallet is discouraged by developers of Bitcoin Core.
Figure shows a nondeterministic wallet, containing a loose collection of random keys. In a deterministic wallet, the seed is sufficient to recover all the derived keys, and therefore a single backup at creation time is sufficient. Mnemonic codes are English word sequences that represent encode a random number used as a seed to derive a deterministic wallet.
The sequence of words is sufficient to re-create the seed and from there re-create the wallet and all the derived keys. A wallet application that implements deterministic wallets with mnemonic code will show the user a sequence of 12 to 24 words when first creating a wallet.
Fraudsters Target Discord Users in Cryptocurrency Scam
That sequence of words is the wallet backup and can be used to recover and re-create all the keys in the same or any compatible wallet application. Mnemonic code words make it easier for users to back up wallets because they are easy to read and correctly transcribe, as compared to a random sequence of numbers. Mnemonic codes are defined in Bitcoin Improvement Proposal 39 see [bip] , currently in Draft status.
Note that BIP is a draft proposal and not a standard. Specifically, there is a different standard, with a different set of words, used by the Electrum wallet and predating BIP Table shows the relationship between the size of entropy data and the length of mnemonic codes in words. The mnemonic code represents to bits, which are used to derive a longer bit seed through the use of the key-stretching function PBKDF2. The resulting seed is used to create a deterministic wallet and all of its derived keys. Tables and show some examples of mnemonic codes and the seeds they produce.
Hierarchical deterministic wallets contain keys derived in a tree structure, such that a parent key can derive a sequence of children keys, each of which can derive a sequence of grandchildren keys, and so on, to an infinite depth. This tree structure is illustrated in Figure HD wallets offer two major advantages over random nondeterministic keys.
First, the tree structure can be used to express additional organizational meaning, such as when a specific branch of subkeys is used to receive incoming payments and a different branch is used to receive change from outgoing payments. Branches of keys can also be used in a corporate setting, allocating different branches to departments, subsidiaries, specific functions, or accounting categories. The second advantage of HD wallets is that users can create a sequence of public keys without having access to the corresponding private keys.
This allows HD wallets to be used on an insecure server or in a receive-only capacity, issuing a different public key for each transaction. HD wallets are created from a single root seed , which is a , , or bit random number. Everything else in the HD wallet is deterministically derived from this root seed, which makes it possible to re-create the entire HD wallet from that seed in any compatible HD wallet. This makes it easy to back up, restore, export, and import HD wallets containing thousands or even millions of keys by simply transferring only the root seed. The root seed is most often represented by a mnemonic word sequence , as described in the previous section Mnemonic Code Words , to make it easier for people to transcribe and store it.
The process of creating the master keys and master chain code for an HD wallet is shown in Figure The root seed is input into the HMAC-SHA algorithm and the resulting hash is used to create a master private key m and a master chain code.
Mastering Bitcoin by
The chain code is used to introduce entropy in the function that creates child keys from parent keys, as we will see in the next section. Hierarchical deterministic wallets use a child key derivation CKD function to derive children keys from parent keys. The chain code is used to introduce seemingly random data to the process, so that the index is not sufficient to derive other child keys.
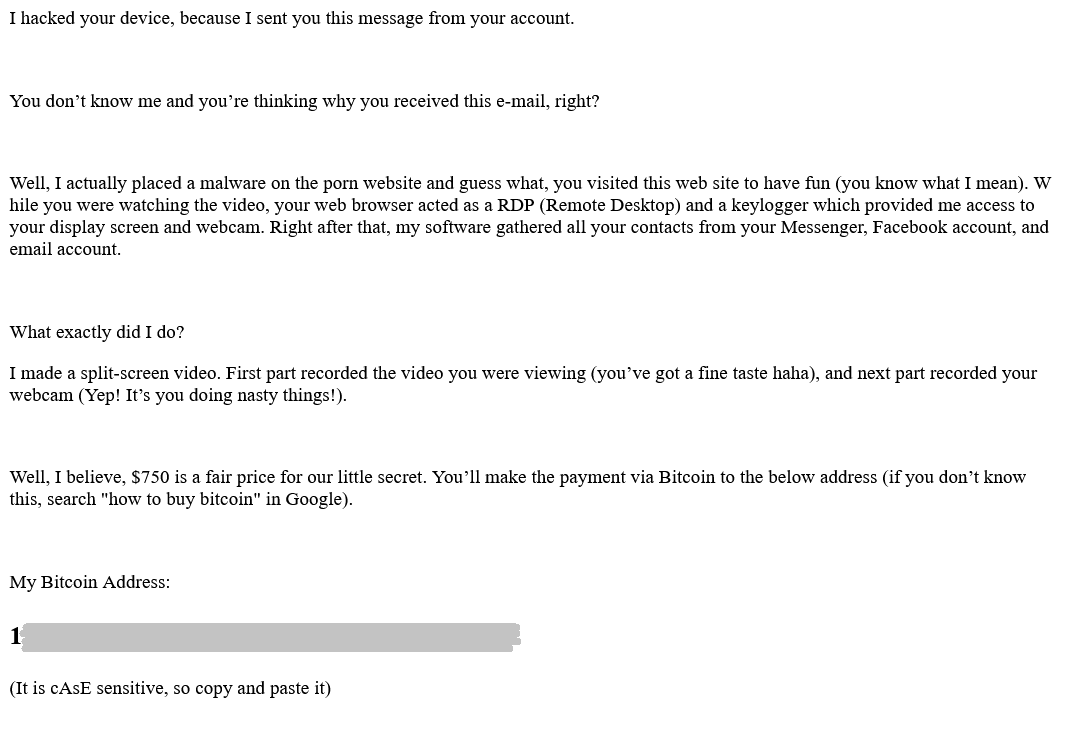 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
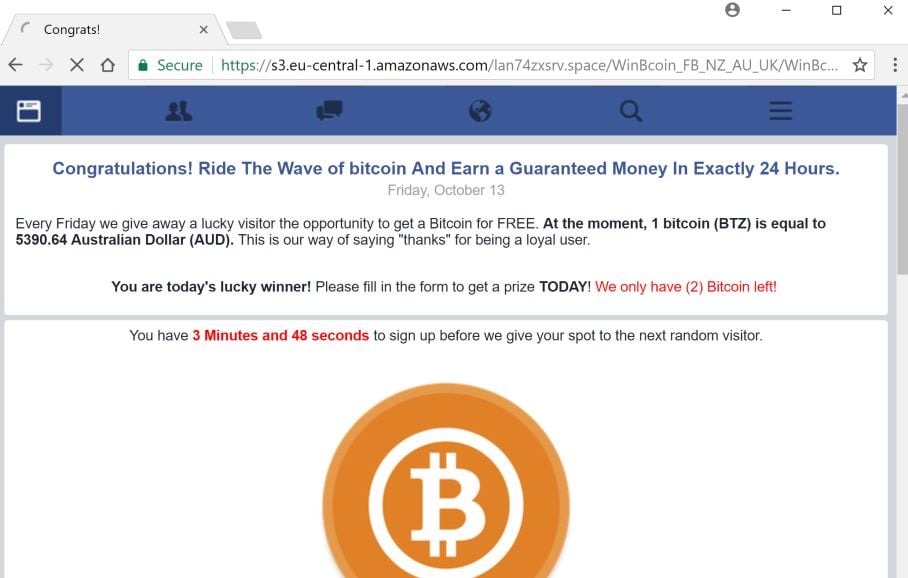 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
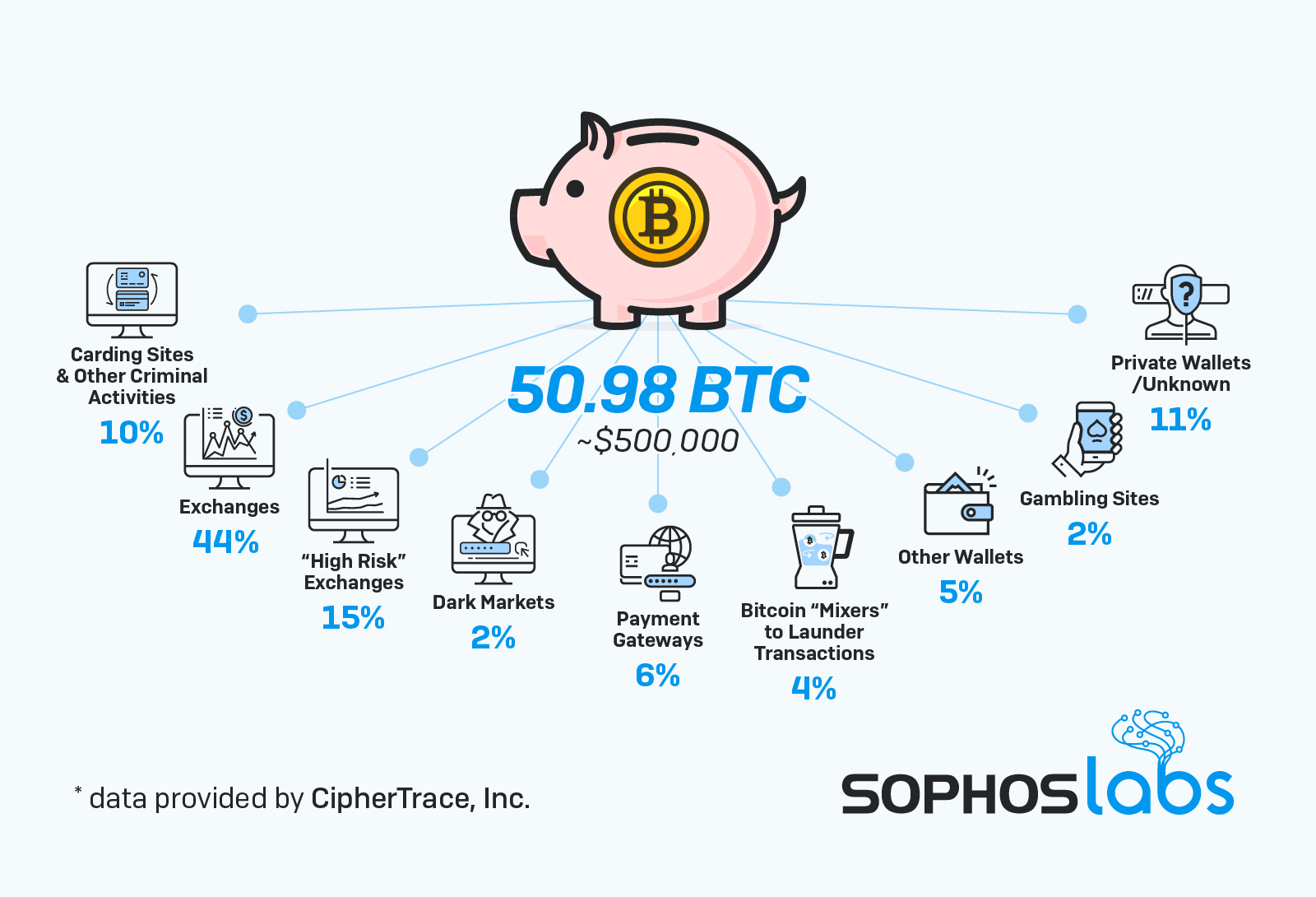 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Bitcoin_Mining_Work_Dec_2020-01-bd91c1773e5d4320b9b0e3cee1ecc4fd.jpg) Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
 Randomly received bitcoin
Randomly received bitcoin
Related randomly received bitcoin
Copyright 2020 - All Right Reserved