/coinmetricsbtchalving-1aa1b4c4ddea47cfbe0439daf6e3626e.jpg)
Trust Wallet. Ask Academy. Bitcoin Halving Countdown. Current block height. Blocks until halving. BTC Price. What is a block halving? Why are halvings significant? How many Bitcoin halvings have there been previously? Halving Est. How does the Bitcoin block halving work? How is our timer calculated?
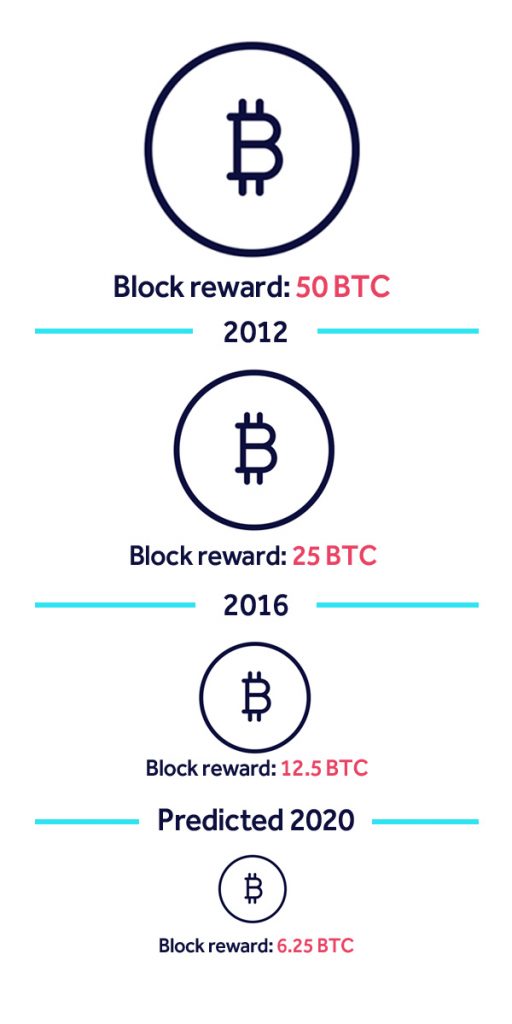
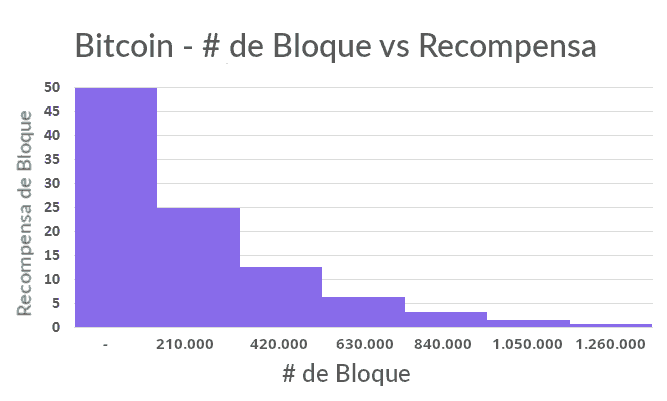
Detailed datasheet Total BTC in circulation. Total BTC to ever be produced. Percentage of BTC mined. BTC generated each day. At the time of writing, there are 18,, Bitcoins already in circulation, leaving just 2,, left to be released via mining rewards. In , the reward for each block in the chain mined was 50 Bitcoins. After the first halving it was 25, then If gold's value is based on its scarcity, then a "halving" of gold output every four years would theoretically drive its price higher. These halvings reduce the rate at which new coins are created and thus lower the available supply.
This can cause some implications for investors as other assets with low supply, like gold, can have high demand and push prices higher. In the past, these Bitcoin halvings have correlated with massive surges in Bitcoin's price. The second Bitcoin halving occurred in July of The theory of the halving and the chain reaction that it sets off works something like this:.
In the event that a halving does not increase demand and price, then miners would have no incentive as the reward for completing transactions would be smaller and the value of Bitcoin would not be high enough. To prevent this, Bitcoin has a process to change the difficulty it takes to get mining rewards, or, in other words, the difficulty of mining a transaction.
In the event that the reward has been halved and the value of Bitcoin has not increased, the difficulty of mining would be reduced to keep miners incentivized. This means that the quantity of Bitcoin released as a reward is still smaller but the difficulty of processing a transaction is reduced. This process has proven successful twice.
So far, the result of these halvings has been a ballooning in price followed by a large drop. The crashes that have followed these gains, however, have still maintained prices higher than before these halving events.
What is bitcoin halving and will it affect the rate?
While this system has worked so far, the halving is typically surrounded by immense speculation, hype, and volatility, and it is unpredictable as to how the market will react to these events in the future. The term "halving" as it relates to Bitcoin has to do with how many bitcoin tokens are found in a newly created block. Today, there have been three halving events and a block only contains 6. When the next halving occurs, a block will only contain 3. The first Bitcoin "halvening" occurred on November 28, , after a total of 5,, BTC had been mined. The next occurred on July 9, , and the latest on May 11, The next is expected to occur in the Spring of The Bitcoin mining algorithm is set with a target of finding new blocks once every ten minutes.
However, if more miners join the network and add more hashing power, the time to find blocks will decrease. This is remedied by resetting the mining difficulty, or how hard it is for a computer to solve the mining algorithm, once every two weeks or so to restore a minute target. As the Bitcoin network has grown exponentially over the past decade, the average time to find a block has consistently been below 10 minutes roughly 9. Since halving the block reward effectively doubles the cost to miners, who are essentially the producers of bitcoins, it should have a positive impact on price since producers will need to adjust their selling price to their costs.
Empirical evidence does show that Bitcoin price tends to rise in anticipation of a halvening, often several months prior to the actual event. Around the year , the last of the 21 million bitcoin ever to be mined will have been. At this point, the halving schedule will cease, since there will be no more new bitcoins to be found.
Miners, however, will still be incentivized to continue validating and confirming new transactions on the blockchain since the value of transaction fees paid to miners is thought to rise into the future.
The reasons being a greater transaction volume that have fees attached, plus a greater nominal market value of bitcoins. Bitcoin Wiki. Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.
Bitcoin 'halving': What does the much-hyped event mean?
At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification.
I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses.
Navigation menu
Bitcoin Guide to Bitcoin. Cryptocurrency Bitcoin. What Is a Bitcoin Halving? Key Takeaways A Bitcoin halving event is when the reward for mining Bitcoin transactions is cut in half. This event also cuts in half Bitcoin's inflation rate and the rate at which new Bitcoins enter circulation.
Bitcoin Halving
Both previous halvings have correlated with intense boom and bust cycles that have ended with higher prices than prior to the event. Bitcoin last halved on May 11, , around 3 pm EST, resulting in a block reward of 6. Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy.
Compare Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Terms Bitcoin Bitcoin is a digital or virtual currency created in that uses peer-to-peer technology to facilitate instant payments.
It follows the ideas set out in a whitepaper by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto, whose true identity has yet to be verified.
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/coinmetricsbtchalving-1aa1b4c4ddea47cfbe0439daf6e3626e.jpg) Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
 Bitcoin halving block
Bitcoin halving block
Related bitcoin halving block
Copyright 2020 - All Right Reserved