
Why is my cryptocurrency transaction pending? To verify if your transaction has already been confirmed on the blockchain, please select the transaction on Uphold, and click on the " Blockchain Transaction ID " link: A blockchain transaction typically requires 3 confirmations for deposits and 1 confirmation for withdraws: The bitcoin network sometimes experiences a slowdown, as miners take longer to include transactions within the mempool into new blocks.
Was this article helpful? Web classic view How to add funds using debit or credit card Web Classic view Is Uphold a free service?
Today, the fees represent 0. However, as the reward decreases over time and the number of transactions per block increases, a greater proportion of bitcoin mining earnings will come from fees. After , all bitcoin miner earnings will be in the form of transaction fees.
By evoking the extraction of precious metals, it focuses our attention on the reward for mining, the new bitcoins in each block. Although mining is incentivized by this reward, the primary purpose of mining is not the reward or the generation of new coins. If you view mining only as the process by which coins are created, you are mistaking the means incentives as a goal of the process.
Mining is the main process of the decentralized clearinghouse, by which transactions are validated and cleared. Mining secures the bitcoin system and enables the emergence of network-wide consensus without a central authority. Mining is the invention that makes bitcoin special, a decentralized security mechanism that is the basis for peer-to-peer digital cash. The reward of newly minted coins and transaction fees is an incentive scheme that aligns the actions of miners with the security of the network, while simultaneously implementing the monetary supply.
Each block, generated on average every 10 minutes, contains entirely new bitcoins, created from nothing. For the first four years of operation of the network, each block contained 50 new bitcoins. In November , the new bitcoin issuance rate was decreased to 25 bitcoins per block and it will decrease again to Finally, after Thereafter, blocks will contain no new bitcoins, and miners will be rewarded solely through the transaction fees. Figure shows the total bitcoin in circulation over time, as the issuance of currency decreases. In the example code in Example , we calculate the total amount of bitcoin that will be issued.
Example shows the output produced by running this script.
How does a block chain prevent double-spending of Bitcoins?
The finite and diminishing issuance creates a fixed monetary supply that resists inflation. Unlike a fiat currency, which can be printed in infinite numbers by a central bank, bitcoin can never be inflated by printing. The most important and debated consequence of a fixed and diminishing monetary issuance is that the currency will tend to be inherently deflationary.
Deflation is the phenomenon of appreciation of value due to a mismatch in supply and demand that drives up the value and exchange rate of a currency. The opposite of inflation, price deflation means that the money has more purchasing power over time. Many economists argue that a deflationary economy is a disaster that should be avoided at all costs. That is because in a period of rapid deflation, people tend to hoard money instead of spending it, hoping that prices will fall. Bitcoin experts argue that deflation is not bad per se.
Rather, deflation is associated with a collapse in demand because that is the only example of deflation we have to study. In a fiat currency with the possibility of unlimited printing, it is very difficult to enter a deflationary spiral unless there is a complete collapse in demand and an unwillingness to print money. Deflation in bitcoin is not caused by a collapse in demand, but by a predictably constrained supply. In practice, it has become evident that the hoarding instinct caused by a deflationary currency can be overcome by discounting from vendors, until the discount overcomes the hoarding instinct of the buyer.
Because the seller is also motivated to hoard, the discount becomes the equilibrium price at which the two hoarding instincts are matched. It remains to be seen whether the deflationary aspect of the currency is really a problem when it is not driven by rapid economic retraction. In the previous chapter we looked at the blockchain, the global public ledger list of all transactions, which everyone in the bitcoin network accepts as the authoritative record of ownership.
All traditional payment systems depend on a trust model that has a central authority providing a clearinghouse service, basically verifying and clearing all transactions. Bitcoin has no central authority, yet somehow every full node has a complete copy of a public ledger that it can trust as the authoritative record. The blockchain is not created by a central authority, but is assembled independently by every node in the network. Somehow, every node in the network, acting on information transmitted across insecure network connections, can arrive at the same conclusion and assemble a copy of the same public ledger as everyone else.
Chapter 8. Mining and Consensus
This chapter examines the process by which the bitcoin network achieves global consensus without central authority. Emergent, because consensus is not achieved explicitly—there is no election or fixed moment when consensus occurs. Instead, consensus is an emergent artifact of the asynchronous interaction of thousands of independent nodes, all following simple rules. All the properties of bitcoin, including currency, transactions, payments, and the security model that does not depend on central authority or trust, derive from this invention.
In the next few sections we will examine these processes and how they interact to create the emergent property of network-wide consensus that allows any bitcoin node to assemble its own copy of the authoritative, trusted, public, global ledger. In Chapter 5 , we saw how wallet software creates transactions by collecting UTXO, providing the appropriate unlocking scripts, and then constructing new outputs assigned to a new owner. The resulting transaction is then sent to the neighboring nodes in the bitcoin network so that it can be propagated across the entire bitcoin network.
However, before forwarding transactions to its neighbors, every bitcoin node that receives a transaction will first verify the transaction. This ensures that only valid transactions are propagated across the network, while invalid transactions are discarded at the first node that encounters them.
- bitcoin wallet address kaise banaye.
- Bitcoin Transaction not Found on Blockchain Solution.
- Transactions — Bitcoin.
Each node verifies every transaction against a long checklist of criteria:. Note that the conditions change over time, to address new types of denial-of-service attacks or sometimes to relax the rules so as to include more types of transactions. By independently verifying each transaction as it is received and before propagating it, every node builds a pool of valid new transactions the transaction pool , roughly in the same order.
Bitcoin Developer Reference - Bitcoin
Some of the nodes on the bitcoin network are specialized nodes called miners. In Chapter 1 we introduced Jing, a computer engineering student in Shanghai, China, who is a bitcoin miner. Unlike Jing, some miners mine without a full node, as we will see in Mining Pools. However, the arrival of a new block has special significance for a mining node. The competition among miners effectively ends with the propagation of a new block that acts as an announcement of a winner. To miners, receiving a new block means someone else won the competition and they lost.
However, the end of one round of a competition is also the beginning of the next round. The new block is not just a checkered flag, marking the end of the race; it is also the starting pistol in the race for the next block. After validating transactions, a bitcoin node will add them to the memory pool , or transaction pool , where transactions await until they can be included mined into a block. The arrival of this block signifies the end of the competition for block , and the beginning of the competition to create block , By now it has collected a few hundred transactions in the memory pool.
Whatever transactions remain in the memory pool are unconfirmed and are waiting to be recorded in a new block. This block is called a candidate block because it is not yet a valid block, as it does not contain a valid proof of work. The block becomes valid only if the miner succeeds in finding a solution to the proof-of-work algorithm. Prioritized transactions can be sent without any fees, if there is enough space in the block. The priority of a transaction is calculated as the sum of the value and age of the inputs divided by the total size of the transaction:. The size of the transaction is measured in bytes.
The first 50 kilobytes of transaction space in a block are set aside for high-priority transactions.
Introduction
This allows high-priority transactions to be processed even if they carry zero fees. Some miners choose to mine transactions without fees on a best-effort basis. Other miners may choose to ignore transactions without fees. Any transactions left in the memory pool, after the block is filled, will remain in the pool for inclusion in the next block. Eventually a transaction without fees might reach a high enough priority to be included in the block for free.
Bitcoin transactions do not have an expiration time-out. A transaction that is valid now will be valid in perpetuity. However, if a transaction is only propagated across the network once, it will persist only as long as it is held in a mining node memory pool. When a mining node is restarted, its memory pool is wiped clear, because it is a transient non-persistent form of storage. Although a valid transaction might have been propagated across the network, if it is not executed it may eventually not reside in the memory pool of any miner.
Wallet software is expected to retransmit such transactions or reconstruct them with higher fees if they are not successfully executed within a reasonable amount of time. You can see this block in the blockchain using the Bitcoin Core client command-line interface, as shown in Example The first transaction added to the block is a special transaction, called a generation transaction or coinbase transaction. Unlike regular transactions, the generation transaction does not consume spend UTXO as inputs.
Instead, it has only one input, called the coinbase , which creates bitcoin from nothing. The output of the generation transaction sends the value of The fees are calculated as:. The reward is calculated based on the block height, starting at 50 bitcoins per block and reduced by half every , blocks. Because this block is at height ,, the correct reward is 25 bitcoins.
- tt 139 btc 2021.
- notowania bitcoin online.
- Documentation Structure?
The initial subsidy is calculated in satoshis by multiplying 50 with the COIN constant ,, satoshis. This sets the initial reward nSubsidy at 5 billion satoshis. Next, the function calculates the number of halvings that have occurred by dividing the current block height by the halving interval SubsidyHalvingInterval.
 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
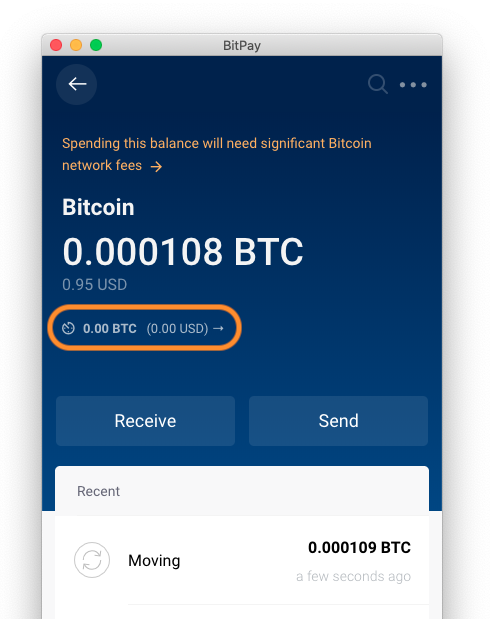 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
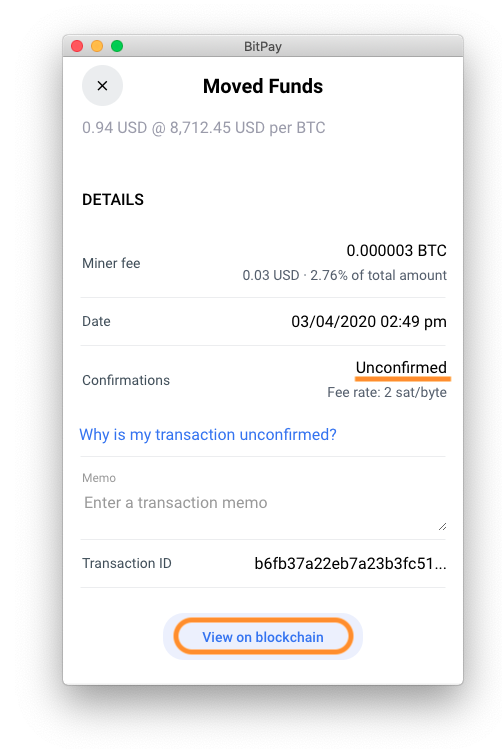 Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Bitcoin transaction hash not found
Related bitcoin transaction hash not found
Copyright 2020 - All Right Reserved